Hello everyone, I am using the Method of Moments (MoM) to study the electromagnetic scattering of PEC metal spheres. I found that when the direction of my plane wave propagation is (0,0,-1) and the polarization direction is (-1,0,0), the RCS (Radar Cross Section) plot I generated is different from the one I obtained using FEKO. However, when I use the plane wave propagation direction (-1,0,0) and polarization direction (0,0,-1) (i.e., reversed), I get results that match the FEKO simulation. I would like to know if there is a problem with my code or approach? I would greatly appreciate it if anyone who understands could let me know. My BEMPP version is the latest. The code and results are as follows.
import bempp_cl.api
import numpy as np
bempp_cl.api.enable_console_logging()
grid = bempp_cl.api.shapes.regular_sphere(3)
frequency = 3e8 # 300Mhz #PEC
eps0 = 8.854187817e-12
mu0 = 4 * np.pi * 1e-7
zf0 = np.sqrt(mu0/eps0)
k = 2np.pifrequencynp.sqrt(eps0mu0)
#polarization = np.array([0, 0, -1.0])
#direction = np.array([-1.0, 0, 0])
polarization = np.array([-1.0, 0, 0])
direction = np.array([0, 0, -1.0])
def plane_wave(point):
return polarization * np.exp(-1j * k * np.dot(point, direction))
@bempp_cl.api.complex_callable
def tangential_trace(point, n, domain_index, result):
value = polarization * np.exp(-1j * k * np.dot(point, direction))result[:]
=np.cross(value, n)
div_space = bempp_cl.api.function_space(grid, “RWG”, 0)
curl_space = bempp_cl.api.function_space(grid, “SNC”, 0)
from bempp_cl.api.operators.boundary import maxwellelec = bempp_cl.api.operators.boundary.maxwell.electric_field(div_space, div_space, curl_space, k)
trace_fun = bempp_cl.api.GridFunction(div_space, fun = tangential_trace, dual_space = curl_space)
from bempp_cl.api.linalg import lu
lambda_data = lu(elec, trace_fun)
try:
get_ipython().run_line_magic(“matplotlib”, “inline”)
ipython = True
except NameError:
ipython = False
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import make_axes_locatable
from matplotlib.patches import Circle
number_of_angles = 400
angles = np.pi * np.linspace(0, 1, number_of_angles)
#unit_points = np.array([np.zeros(number_of_angles), np.cos(angles), np.sin(angles)]) #yz
unit_points = np.array([np.cos(angles), np.zeros(number_of_angles), np.sin(angles)]) #xz
#unit_points = np.array([np.cos(angles), np.sin(angles), np.zeros(number_of_angles)]) #xy平面
far_field = np.zeros((3, number_of_angles), dtype=“complex128”)
electric_field=bempp_cl.api.operators.far_field.maxwell.electric_field(lambda_data.space, unit_points, k)
far_field = -electric_field * lambda_data
plt.rcParams[“figure.figsize”] = (10, 8)
# Resize the figure
cross_section = 10 * np.log10(4 * np.pi * np.sum(np.abs(far_field) ** 2, axis=0))
plt.plot(angles * 180 / np.pi, cross_section)plt.title(“Scattering Cross Section [dB]”)_ = plt.xlabel(“Angle (Degrees)”)
plt.show()
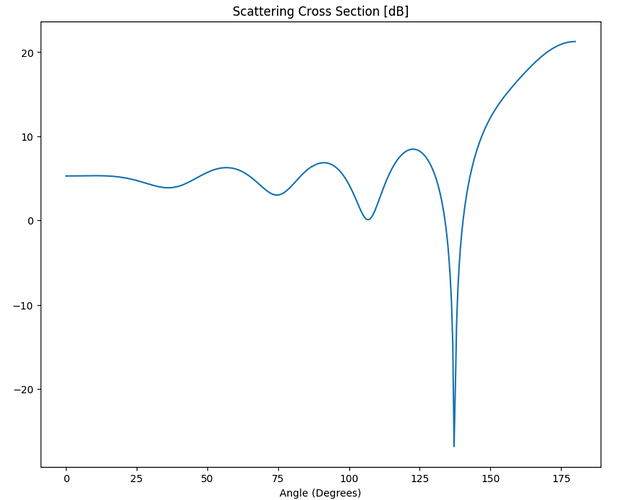
This is the result, but it is not the correct RCS for the plane wave.
Although the results below are correct, they correspond to the case where the polarization direction and the propagation direction are reversed.